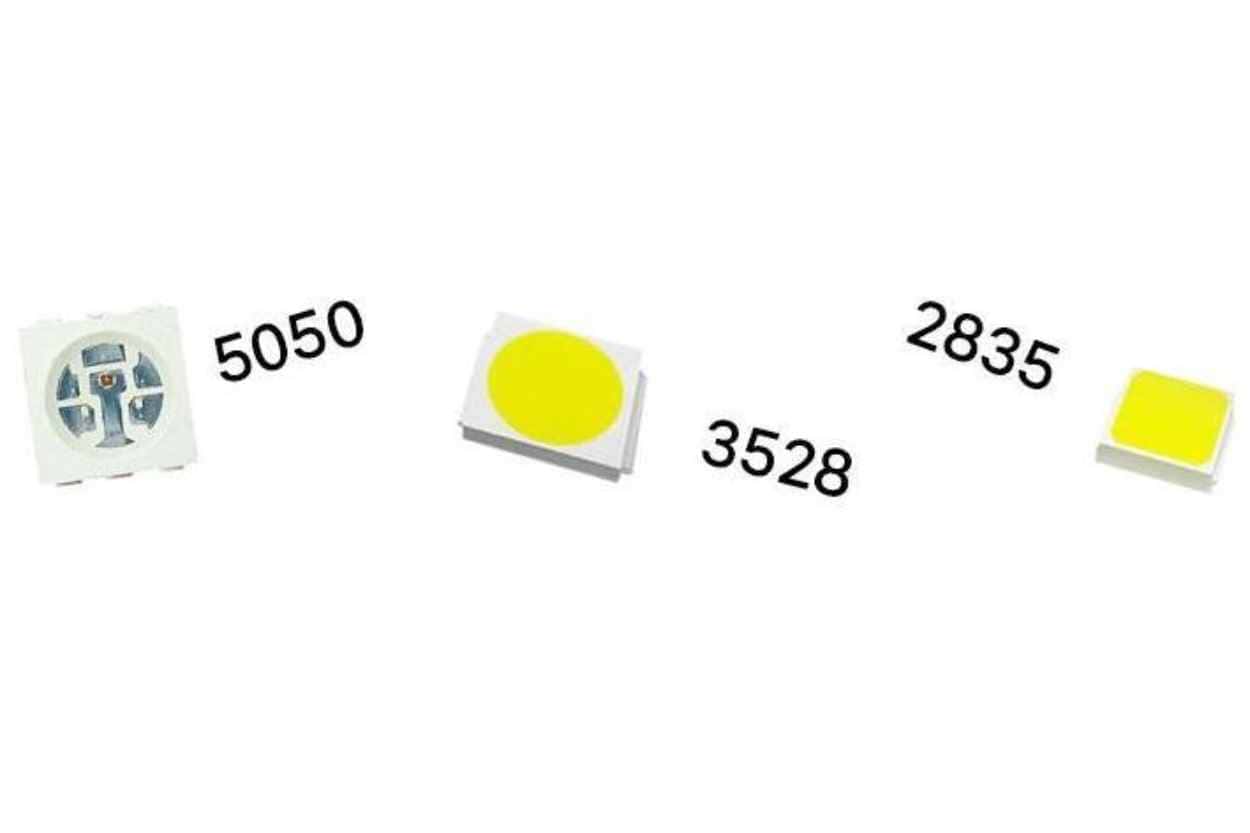
In the world of LED lighting, choosing the right type of LED strip light is crucial for your project. You’re likely to come across a variety of model numbers that signify the size and characteristics of LED chips, among which 2835, 3528, and 5050 are common options. These numbers aren’t just random; they represent the physical dimensions of the LED chips, affecting their performance and suitability for different applications.
Fundamentals of LED Strip Lighting
When you’re exploring LED strip lighting, it’s essential to understand the basics. LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. LED strips are flexible circuit boards populated with LEDs that you can stick almost anywhere you want to add powerful lighting in a variety of colors and brightnesses.
Types of LED Strips:
- Single Color: Offers lighting in a single, static color.
- RGB (Red, Green, Blue): Allows you to mix colors and choose from a wide spectrum.
- RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White): Includes all the features of RGB with an additional white light for purer white tones.
Key Components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| LEDs | Provide the actual light source in various color options. |
| Resistors | Ensure LEDs operate at the correct voltage to prevent damage. |
| Controller | Allows you to change the color, brightness, and patterns on RGB/RGBW strips. |
| Power Supply | Converts main voltage to a lower voltage that LED strips can use. |
The numbers (2835, 3528, 5050, etc.) refer to the size of the LEDs on the strip. For example, a 5050 LED is 5.0mm x 5.0mm. The size can influence the brightness and energy consumption of the LED strip.
Brightness and Power:
- Larger LEDs generally emit more light and require more power.
- Brightness is measured in lumens, and LED strips will vary in lumen output.
- Power requirement, denoted as watts per meter, indicates how much power the strip consumes for a set length.
Installation Tips:
- Ensure your LED strip has the correct IP rating for your intended use (e.g., IP65 for water resistance).
- Mounting surfaces should be clean and stable.
- Proper heat dissipation is essential; avoid enclosed spaces without airflow.
To select the ideal LED strip for your project, consider the required brightness, color options, and installation location.
Overview of LED Chip Types
In this section, you’ll learn about the specific characteristics and uses of various LED chip models, namely the 2835, 3528, and 5050.
2835 LED Chips
2835 LEDs are known for their relatively small size and efficient heat dissipation. They measure 2.8mm by 3.5mm and are often used in lighting applications where space is limited but high efficiency is required.
- Voltage: Typically 2.8–3.4V
- Current: Around 150mA
- Luminous Efficacy: High, due to improved thermal management
3528 LED Chips
3528 LEDs are older than 2835 and 5050 chips and are considered a standard size in the industry. They are 3.5mm by 2.8mm and are a common choice for moderate illumination tasks.
- Voltage: Usually 2.8–3.4V
- Current: Generally 20mA
- Brightness: Moderate; suitable for various lighting applications
5050 LED Chips
The 5050 LEDs are larger, with dimensions of 5.0mm by 5.0mm, making them suitable for applications where brighter light is needed. They have three light-emitting diodes in one housing, which allows them to produce a wide range of colors, including RGB.
- Voltage: Typically 2.8–3.4V per diode
- Current: About 60mA per diode
- Color Options: Wide range due to RGB capabilities
Physical Characteristics
In this section, you’ll find detailed information about the physical differences between the 2835, 3528, and 5050 LED chip types.
Sizes and Shapes
The 2835, 3528, and 5050 numbers refer to the size dimensions of the LED chips. The 2835 has dimensions of 2.8mm by 3.5mm. The 3528 is slightly larger, measuring 3.5mm by 2.8mm. The 5050 is the largest of the three, with each chip measuring 5.0mm by 5.0mm. All three models typically come in a rectangular shape, but the area they cover varies due to their differing sizes.
Chip Dimensions
Here’s a quick comparison of the chip dimensions for each LED type:
- 2835 LED
- Length: 2.8mm
- Width: 3.5mm
- 3528 LED
- Length: 3.5mm
- Width: 2.8mm
- 5050 LED
- Length: 5.0mm
- Width: 5.0mm
Each chip type is designed for specific applications, and your choice will depend on the required brightness, energy efficiency, and installation considerations. The larger 5050 chips are typically brighter due to their size, but the smaller 2835 and 3528 chips can be a better choice for applications with limited space or where less light is needed.
Brightness and Light Output
When comparing LED strip lights—2835, 3528, and 5050—brightness is a key factor. Brightness in LEDs is measured in lumens. The higher the lumens, the brighter the LED.
2835 LEDs are known for their higher efficiency. For each watt of power, you get more lumens compared to 3528 LEDs. This makes 2835 LEDs brighter per watt and an energy-saving option.
3528 LEDs are older and generally less bright than 2835 and 5050 LEDs. They are suitable for accent lighting where high brightness is not the priority.
5050 LEDs have a large surface area, providing a broader angle of light. Each 5050 LED is significantly brighter than one 3528 or 2835 LED, thanks to their larger size and ability to house three times the diodes.
Here is a comparison table summarizing the differences:
| LED Type | Lumens per LED (approx.) | Power Usage | Brightness Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2835 | 22-24 | Low | High Efficiency |
| 3528 | 6-8 | Very Low | Moderate |
| 5050 | 18-20 | Medium | High |
Note: These values are approximate and can vary based on manufacturer and LED binning.
In summary, select 2835 LEDs for energy-efficient, bright solutions, 3528 LEDs for less critical applications, and 5050 LEDs for situations where maximum brightness is required. Your choice should align with your specific lighting needs.
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
When assessing LED strip lights such as 2835, 3528, and 5050, it’s crucial to consider the Color Rendering Index (CRI). This metric rates the ability of a light source to accurately display the colors of different objects compared to a natural light source. The CRI is measured on a scale from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating better color accuracy.
Here are some key points you need to know about CRI:
- High-CRI LEDs: They produce more accurate colors, which is essential in settings where color differentiation is important, such as art studios or retail stores.
- LED Strip CRI Ratings: Typically, LED strips like the 2835, 3528, and 5050 series can have CRI ratings ranging from below 80 to above 90, with the higher numbers being desirable for most applications.
- CRI Impact: With a higher CRI LED strip, you can expect to see colors that are more vibrant and true to life.
Use this table as a quick reference guide:
| CRI Rating | Color Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 90+ | Excellent |
| 80-89 | Good |
| 70-79 | Fair |
| Below 70 | Poor |
Keep in mind that while CRI is an important factor, it’s not the only aspect to consider when choosing between different LED strips. However, knowing the CRI can greatly influence your decision, especially if your project requires precise color rendering. Ensure you check the product specifications for the CRI rating to match your needs.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
When comparing LED chip types—2835, 3528, and 5050—it’s crucial to consider their power consumption and efficiency. Each model has a different energy footprint due to variances in size and design.
- 2835 LEDs: You’ll find these to be highly efficient with a low power consumption. They typically use around 0.2 watts per chip. Because of their improved design, these LEDs offer higher lumen output per watt, translating into better energy utilization.
- 3528 LEDs: These older models consume approximately 0.08 watts per chip. While they consume less power, they also produce less light compared to the 2835 and 5050, resulting in lower overall efficiency.
- 5050 LEDs: These are larger chips that consume around 0.24 watts per chip. Their design allows them to emit a broader beam of light, but this comes at the cost of higher power usage.
Here is a simple comparison table for clarity:
| LED Type | Power Consumption (per chip) | Relative Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| 2835 | 0.2W | High |
| 3528 | 0.08W | Moderate |
| 5050 | 0.24W | Low-Moderate |
Keep in mind:
- The efficiency of an LED is determined by the lumens produced per watt of electricity used.
- Your specific application needs will dictate which LED type is the most energy-efficient choice for you.
- Advances in technology may lead to improvements in efficiency and reduction in power consumption across all types.
Heat Dissipation
In LED strip lighting, your choice between 2835, 3528, and 5050 LED chip formats affects heat dissipation. 2835 LEDs are known for their efficient heat dissipation due to a larger heat sink compared to the 3528. This means you’ll enjoy a longer lifespan for your 2835 LED strips as they manage heat better, reducing the risk of overheating.
For the 3528 LEDs, they are smaller and have less surface area for heat dissipation. However, they typically generate less heat to start with due to their smaller size and lower power consumption. When using 3528 LEDs, you should ensure proper ventilation to aid in heat management.
5050 LEDs are larger and can produce more brightness, which in turn generates more heat. The design of the 5050 includes a larger surface area which helps in spreading out the heat. However, they still need to be mounted on a surface that helps dissipate heat effectively.
Here’s a simple comparison:
| LED Type | Size | Heat Sink Area | Heat Generated | Heat Management Needs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2835 | Smaller | Larger (Efficient) | Moderate | Minimal due to efficient design |
| 3528 | Small | Smaller | Less | Moderate, depends on ventilation |
| 5050 | Larger | Larger (Spreading) | More | More, due to higher brightness |
You should select the LED type based on your project requirements, considering that efficient heat dissipation is crucial for the longevity and performance of the LED strips.
Durability and Lifespan
When considering LED strip lights, you’ll find three common types: 2835, 3528, and 5050. Each type has a distinct construction which influences its durability and lifespan.
- 2835 LEDs are known for their efficient heat dissipation. This trait helps to extend their lifespan, as overheating is a common cause of LED failure.
- 3528 LEDs, while older than the 2835 and 5050, have a solid track record for durability. However, they might not last as long as the more modern 2835 LEDs due to less efficient heat management.
- 5050 LEDs, on the other hand, are larger and can run hotter than their smaller counterparts. Despite this, they are built to handle the heat and typically have a robust construction, granting them a long lifespan.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| LED Type | Heat Dissipation | Expected Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
| 2835 | Excellent | Up to 50,000 hours |
| 3528 | Good | Up to 40,000 hours |
| 5050 | Moderate | Up to 50,000 hours |
Your maintenance and usage will also heavily influence the durability of these LEDs. Frequent on-off cycles, high ambient temperatures, and exposure to moisture can all shorten the lifespan of any LED light. Therefore, it’s crucial that you follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and use them within the recommended parameters to ensure the longest possible life for your LED strips.
Flexibility of Use
Each LED strip type presents varied levels of flexibility, influencing your choice depending on the application and installation requirements.
Indoor Versus Outdoor Applications
2835 LED Strips: These are generally suitable for indoor use where space is a constraint. Their compact size offers discreet lighting solutions, and they are often used under cabinets or in display cases. However, they may not be as water-resistant as other options, limiting outdoor use.
3528 LED Strips: Ideal for both indoor ambient lighting and outdoor use, provided they have a proper protective coating. The versatility of 3528 strips means you can install them in living rooms as accent lighting or use waterproof versions for garden lighting.
5050 LED Strips: Their robust design makes them excellent for outdoor applications, enjoying wide popularity for decks and patios. The added brightness and color-changing capabilities also recommend them for vibrant indoor setups where more dynamic lighting is desired.
Installation Considerations
- Flexibility: 5050 strips are thicker and less flexible, making them less suited for tight corners or intricate patterns compared to the more bendable 2835 and 3528 strips.
- Heat Dissipation: You’ll need to consider heat management, especially for 5050 LEDs as they generate more heat. Proper heat sinks or mounting surfaces are essential for maintaining longevity.
- Mounting:
LED Type Mounting Surface 2835 Smooth, small-profile areas 3528 Versatile, multiple surfaces 5050 Flat, spacious surfaces - Power Requirements: Be mindful of power requirements as 5050 LEDs will generally consume more power and may require a larger power source, impacting your installation process.
Price Comparison and Value
When comparing the 2835, 3528, and 5050 LED models, you’re likely to notice some variations in price that are correlated with their performance and features.
The 2835 LEDs are typically the most cost-effective, providing adequate brightness for general use while keeping your budget in check. They are a solid choice if you’re looking for value and efficiency in lower-power applications.
3528 LEDs fall in the middle of the spectrum. They’re moderately priced, offering a balanced blend of brightness and power consumption. This makes them a versatile option for both cost and performance.
On the pricier end are the 5050 LEDs. Their cost is justified by their high brightness levels and the ability to display multiple colors, including RGB variants. If you need high-intensity light and color versatility, spending extra on 5050 LEDs can be worthwhile.
| LED Type | Brightness | Power Consumption | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2835 | Low | Low | $ |
| 3528 | Medium | Medium | $$ |
| 5050 | High | High | $$$ |
In review, your choice should be guided by your specific needs. If price is a major concern and you require basic illumination, go for 2835 LEDs. For a middle ground, consider 3528 LEDs. And if you need the brightest option with color-changing capabilities, and budget is less of an issue, 5050 LEDs are your best bet. Remember that investing in the right LED type ensures both satisfaction and value for your specific application.
Common Applications
LED strip lights are versatile in their applications, each type has distinct characteristics suited for different uses. Your selection among 2835, 3528, and 5050 LED chip types will depend on the desired brightness, energy efficiency, and color options.
Residential Lighting
- 2835 LEDs are commonly used for ambient lighting due to their small size, efficiency, and moderate brightness. They are ideal for:
- Under-cabinet lighting
- Cove lighting
- 3528 LEDs find their place in tasks requiring minimal brightness like accent lighting. Common uses include:
- Backlighting
- Display case lighting
- 5050 LEDs are the go-to for vivid color options and higher brightness levels. They excel in:
- Entertainment areas
- Outdoor settings for accent or task lighting
Commercial Lighting
- 2835 LEDs often light up commercial environments requiring subtle illumination without being overpowering:
- Office task lighting
- Hallway and walkway lighting
- 3528 LEDs support locations that use lighting sparingly but require it to be cost-efficient:
- Display shelves
- Highlighting architectural features
- 5050 LEDs, with their robust brightness and color-changing abilities, are tailored for businesses that need to catch the eye:
- Signage and storefront displays
- Club and bar lighting
Automotive and Specialty
- 2835 LEDs are suitable for automotive interiors because they generate less heat and wear well with use:
- Dashboard and instrument lighting
- Cabin lighting
- 3528 LEDs are used in applications with size constraints and lower brightness requirements:
- Motorcycle accent lighting
- Electronic gadget illumination
- 5050 LEDs are preferred in applications that necessitate bold lighting and RGB capabilities:
- Exterior car underglow
- Emergency vehicle lighting
Compatibility With Controllers and Dimmers
When selecting LED strip lights, it’s vital to consider compatibility with controllers and dimmers. 2835, 3528, and 5050 refer to different sizes of LED chips, and they can dictate the compatibility with various control systems. Here is a breakdown:
- 2835 LEDs: These are typically compatible with most dimmers and controllers, provided they are designed for LED technology. Make sure your controller can handle the low power requirements of 2835 LEDs.
- 3528 LEDs: Slightly larger, these LEDs often work with a wide range of dimmers and controllers as well. They may require a different power specification than 2835 LEDs, so check the compatibility with your existing system.
- 5050 LEDs: These are larger and more powerful, which means they might need controllers capable of handling higher currents. For dimming, ensure your dimmer can adjust the light output without flickering, which can be a common issue with higher-powered LEDs.
Controller Types
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Compatible with all three LED types.
- DMX: Suitable for larger installations and can control each size with the appropriate DMX decoder.
- WiFi/Bluetooth: Ensure they have the correct voltage range for your LED type and size.
Dimmer Compatibility
- Leading-Edge: Typically compatible with 5050 LEDs.
- Trailing-Edge: Better suited for 2835 and 3528 LEDs.
- 0-10V or 1-10V: Check compatibility as they vary by manufacturer and model.
Note: Always reference the manufacturer’s specifications for both your LED strips and the controllers/dimmers to ensure proper operation and longevity of your lighting system. Compatibility ensures you achieve the desired light output and effect smoothly and efficiently.
Availability and Sourcing
When you are looking for LED strip lights, the models 2835, 3528, and 5050 refer to the size of the LED chips in millimeters. For example, a 5050 LED is 5.0mm x 5.0mm.
- 2835 LEDs: These are newer in the market but rapidly gaining popularity due to their improved efficiency and brightness at smaller sizes.
- 3528 LEDs: They are older and once the standard, but they are less common now. They may be available in specialty stores or from specific online retailers.
- 5050 LEDs: They are very popular and widely available due to their versatility and the bright light they emit.
When sourcing these LEDs, consider these options:
- Online Marketplaces:
- Amazon
- eBay
- AliExpress
Pros: Wide selection, competitive pricing.
Cons: Shipping times can vary, quality might differ.
- Specialty Electronics Stores:
- Adafruit
- SparkFun
Pros: Curated selection, often higher quality.
Cons: Potentially higher prices, limited stock.
- Direct from Manufacturers:
Pros: Best prices for bulk orders, custom specifications possible.Cons: Minimum order quantities, longer lead times.
Remember that availability can vary regionally, and it’s important to check the supplier’s reputation and the quality of the product before purchasing. Look for reviews and ratings when buying from online marketplaces and seek out technical specifications when ordering from manufacturers or specialty stores to ensure the product meets your needs.
Summary
Understanding the differences between 2835, 3528, and 5050 LED chips will help you make an informed decision when selecting LED strip lights. Each type has its own set of strengths and applications.
For instance, the 3528 model is typically smaller and used for areas that require less luminosity, whereas the 5050 model, being larger in size, is more suitable for spaces that demand higher brightness. Meanwhile, the 2835 model is a newer design that offers improved heat dissipation and efficiency.